Strata Living
May 16, 2022
Life Insurance – Do You Need Additional Cover?
August 16, 2022When it comes to paying or receiving child support, receiving family tax benefits or other income support payments, there’s lots of confusion and misinformation floating around as to what counts as income when Child Support or Centrelink make their assessment. Both work off the concept of ‘adjusted taxable income’ which takes into account not only your salary, but a range of other factors, in determining the amount of income you are assessed as receiving.
Adjusted taxable income includes:
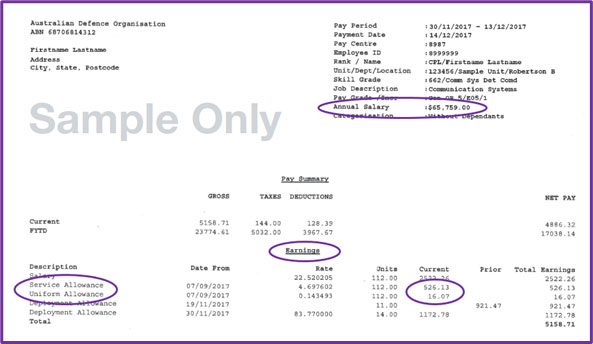
- Taxable income – your gross income minus allowable deductions; including wages and salaries, income from running a business, investment income, taxable income support payments, any taxable Department of Veterans’ Affairs (DVA) payments and Job Keeper payments from your employer.
- Taxable lump sum payments – such as taxable superannuation death benefits, taxable compensation payments, taxable insurance payouts, and superannuation released early (does not include super withdrawals under the First Home Super Saver Scheme or COVID-19 early release of superannuation).
- Foreign income – money you get from outside Australia and don’t pay Australian income tax on. It can include money from foreign business interests, investments or income you earned overseas.
- Tax-exempt foreign income – income from Australia, earned by members of the armed forces serving overseas or Australians on overseas projects approved by the Minister for Trade, Tourism and Investment.
- Total net investment losses – where investment income is less than investment expenses.
- Reportable fringe benefits – pre-tax benefits you get from your employer. They will have been reported on your payment summary at the end of the financial year, or you can ask payroll to tell you the expected amount for this financial year.
- Reportable superannuation contributions – personal super contributions that you made via a salary sacrifice arrangement or that you will claim as an income tax deduction when you lodge your tax return.
- Tax free pensions or benefits – these can include Centrelink payments such as the Disability Support pension or Carer payment, and non-taxable DVA payments such as an Invalidity Service pension, War Widow’s and War Widower’s pension, Partner Service pension, Income Support supplement, Defence Force Income Supplement Allowance (DFISA) where it’s exempt from income tax, and those under the Military Rehabilitation and Compensation Act (MRCA), including arrears and lump sums from Wholly Dependent Partner payments.
- Account-based income stream benefits – may include a deemed amount from an account based income stream if you or your partner are over 60.
For family tax benefits, any child support you pay, including non-cash maintenance like school fees, is deducted from your adjusted taxable income. If you have a partner, their income can also affect your adjusted taxable income.
Warning
This article is a general guide only. It must not be treated as personal financial advice. Each person’s circumstances are different. If you receive income from any source or benefits in lieu of cash money and are unsure about your obligations, you can talk to the relevant agency to find out whether it must be included in the calculation of your adjusted taxable income.
There’s more information at:
https://www.servicesaustralia.gov.au/individuals/topics/what-adjusted-taxable-income/29571
If you make an incomplete declaration, you may incur penalties and be faced with a debt when your payments are recalculated. For more information contact Services Au